Restoring gut flora, also known as the gut microbiota, can be beneficial for overall gut health and digestion.
Did you know that Antibiotics can have a significant impact on gut flora because their main function is to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria, both harmful and beneficial ones. While antibiotics are necessary for treating bacterial infections, they can also disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to a condition called dysbiosis.
Here are some general steps you can take to restore and promote a healthy gut flora:
-
Eat a diverse and balanced diet:
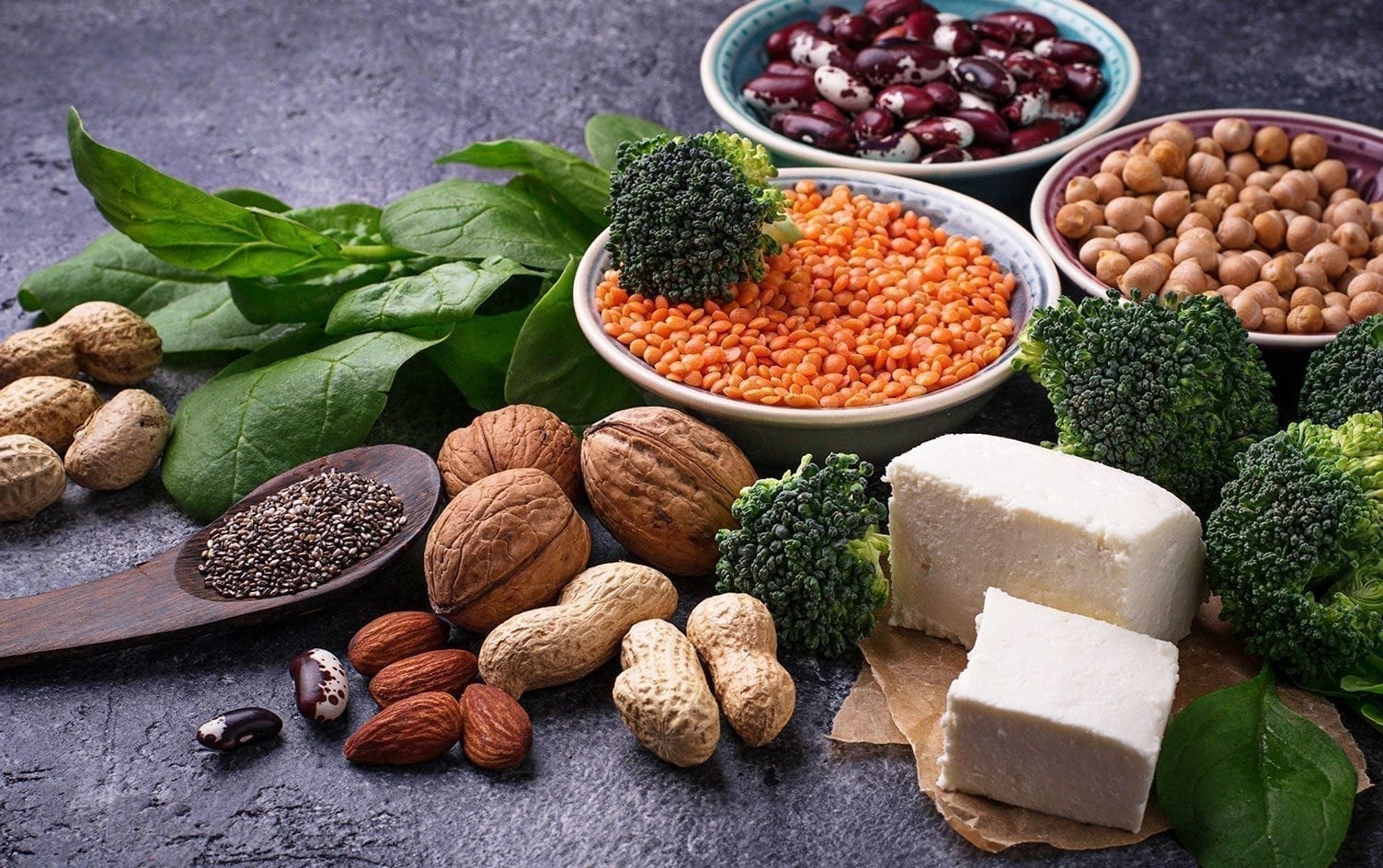 Consume a wide variety of plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods contain fiber, prebiotics, and a range of nutrients that support a healthy gut environment.
Consume a wide variety of plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods contain fiber, prebiotics, and a range of nutrients that support a healthy gut environment.
2. Include fermented foods:
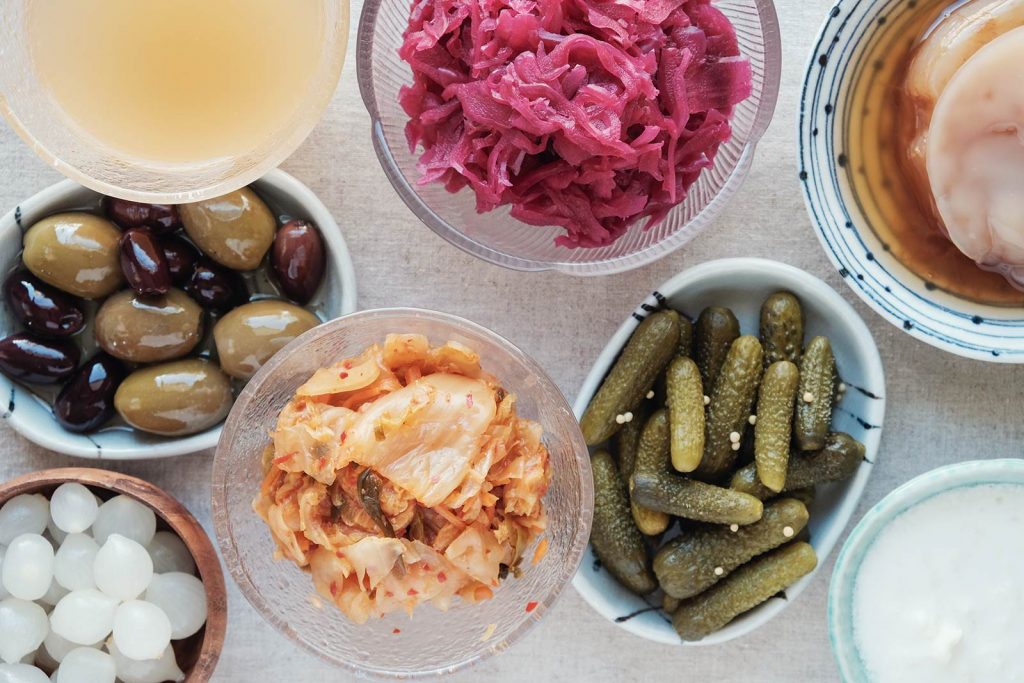 Incorporate fermented foods into your diet, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, tempeh, and miso. These foods contain beneficial bacteria (probiotics) that can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiota.
Incorporate fermented foods into your diet, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, tempeh, and miso. These foods contain beneficial bacteria (probiotics) that can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiota.
3. Avoid excessive antibiotic use:
 Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. Use antibiotics only when necessary and as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. Use antibiotics only when necessary and as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
4. Minimize processed and sugary foods:
 Highly processed foods and excessive sugar intake can negatively impact the gut microbiota. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods and limit added sugars.
Highly processed foods and excessive sugar intake can negatively impact the gut microbiota. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods and limit added sugars.
5. Consider probiotic supplements:

Probiotics are live bacteria that can help replenish beneficial gut flora. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if a probiotic supplement is appropriate for you, and to select a suitable strain and dosage.
6. Manage stress levels:
 Chronic stress can affect the gut microbiota. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and adequate sleep.
Chronic stress can affect the gut microbiota. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and adequate sleep.
7. Stay hydrated:
 Drink enough water to support proper digestion and maintain a healthy gut environment.
Drink enough water to support proper digestion and maintain a healthy gut environment.
8. Avoid unnecessary use of antimicrobial products:
 Overuse of antibacterial soaps, disinfectants, and other antimicrobial products can disturb the gut microbiota. Use them only when necessary and practice good hygiene without excessive antimicrobial products.
Overuse of antibacterial soaps, disinfectants, and other antimicrobial products can disturb the gut microbiota. Use them only when necessary and practice good hygiene without excessive antimicrobial products.
9. Exercise regularly:
 Physical activity can positively influence gut health and promote a diverse gut microbiota. Aim for regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or any activity that gets you moving.
Physical activity can positively influence gut health and promote a diverse gut microbiota. Aim for regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or any activity that gets you moving.
10. Seek professional advice:
 If you have specific gut health concerns or conditions, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance and recommendations.
If you have specific gut health concerns or conditions, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance and recommendations.
Remember that each person’s gut microbiota is unique, and what works for one individual may not work the same for another. It’s important to listen to your body and make adjustments based on your own needs and health goals.